Loading Geo-Trends Review...

GeoWorld Photo Layer
27 August 2025
We are thrilled to introduce a brand-new feature on GeoWorlds GeoMap, the Photo Layer!
Read More
Dimitrios Zekkos
03 Jul 2025
I am excited to have contributed to the #Science paper led by Brian Yannites that was supported by our Center for Land Surface Hazards (#CLaSH) catalyst grant.
Read More
ISSMGE news
04 Jul 2025

Read More

ISSMGE ITT25
24 Jul 2025

Read More

Geoengineer.org news
16 Jul 2025
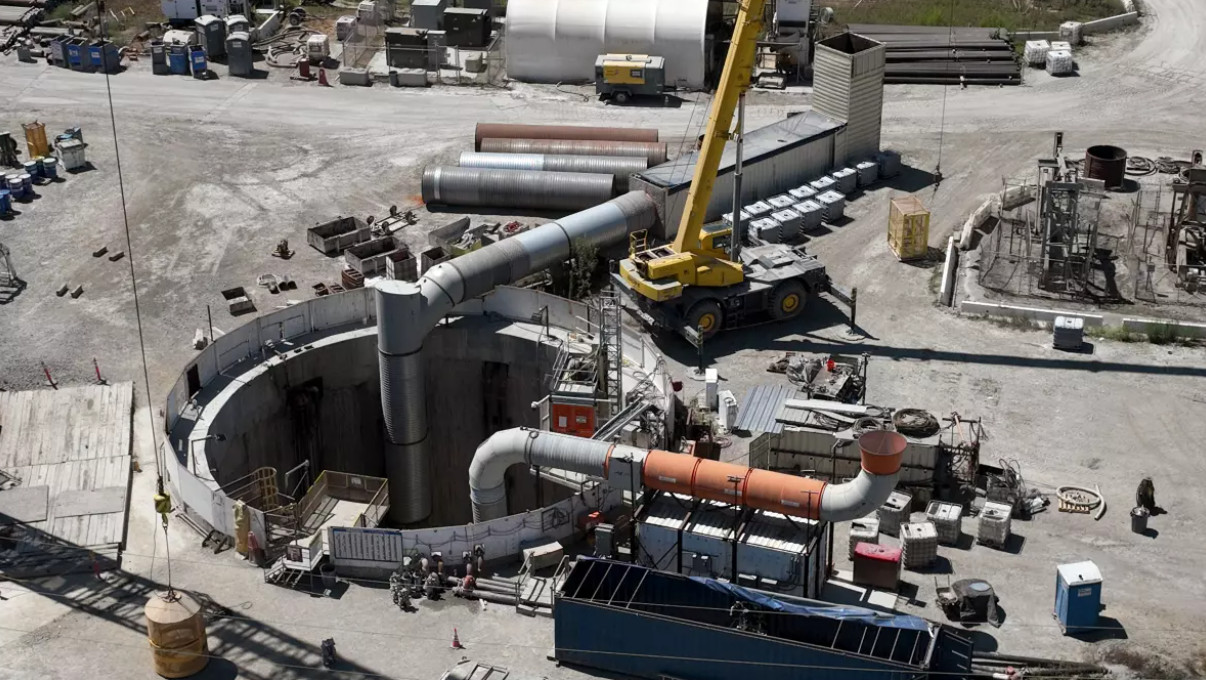

On the evening of July 9, 2025, a structural failure occurred deep beneath Wilmington, Los Angeles, when a section of the Clearwater Tunnel collapsed.
Read More
ISSMGE news
10 Jun 2025
Read More

International Journal of Geoengineering Case Histories news
30 Jun 2025
Read More

GeoWorld GBD
13 August 2025

GeoWorld, with the support of the International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (ISSMGE), is proud to announce the release of the 2025 Geotechnical Business Directory, now in its 11th edition!
Read More
Bentley Systems Going Digital Awards
22 Aug 2025

Bentley Systems, announced the finalists for the subsurface modeling and analysis finalists in the 2025 Going Digital Awards. The awards celebrate the extraordinary achievements of engineers and project teams in advancing infrastructure for better quality of life through digital innovation.
Read More
Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company GeoStudio
12 Jun 2025

GeoStudio 2025.1 offers a balanced mix of new functionalities and enhancements to our core tools. This version introduces Python scripting, enabling more efficient workflows, and 3D reinforcement analysis for better slope stability assessments.
Read More
GeoWorld Corner
18 Jul 2025
We just launched the Nearby Geo-Professional Recommendation Card, now available on the Activity page of the GeoWorld web version.
Read More
Geoengineer.org Discrete Element
28 Aug 2025

The Discrete Element Method (DEM) is a computational technique that has become indispensable in analyzing rockfall dynamics from steep and overhanging slopes. Unlike continuum-based approaches, DEM models material as a collection of discrete particles or rigid bodies, allowing detailed simulation of rock block detachment, free-fall, bouncing, and eventual impact with structures or terrain features. This modeling capacity is especially important for evaluating risk to critical infrastructure such as bridges, roads, and tunnels situated in mountainous regions.
Read More
Geoengineer.org news
09 Mar 2025
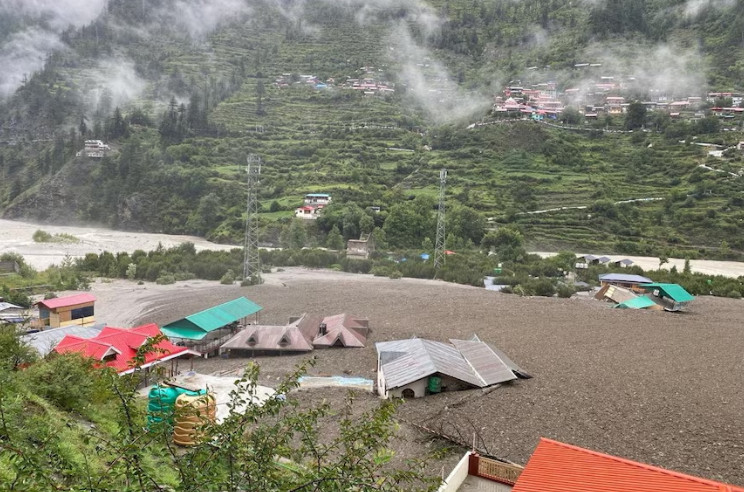

Recent weeks have seen intense rainfall triggering destructive mudslides in two mountainous regions, Uttarakhand in India and Kabardino-Balkaria in Russia.
Read More
DCOdes news
27 Aug 2025
The Analysis of Coal Pillar Stability (ACPS) software, developed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), is a widely adopted tool for assessing coal pillar stability in room-and-pillar mining systems. It is used in both single and multiple seam evaluations, providing engineers and mine planners with a reliable method to minimize the risk of collapses, roof falls, and pillar failures.
Read More
ISSMGE Bulletin
26 Jun 2025
Read More

CEEcareers Careers
03 Jul 2025
For students and early-career professionals in civil and geotechnical engineering, finding the right opportunities can be challenging. General job boards often dont capture the technical and specializ...
Read More
UC Berkeley Geosystems Group award
12 Aug 2025

Read More

Geoengineer.org news
05 Aug 2025
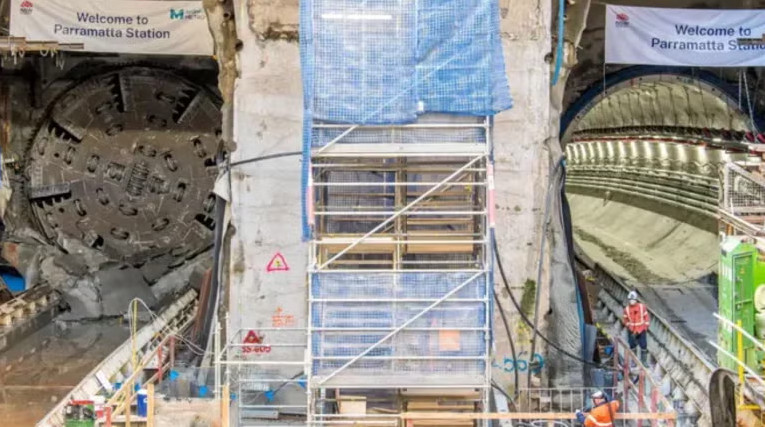

The Sydney Metro West project reached a major tunnelling milestone with the arrival of tunnel-boring machine (TBM) Dorothy at the Parramatta station box.
Read MoreEN 13286-4:2021 Vibrating Hammer Performance Check
Q&A
- 26 Jul 2025
Hi All,
I'm working as a Consultant Engineer a query has arising on a project in relation to the Vibrating Hammer Check as described in Annex A of EN 13286-4:2021. This check requires a minimum dry density of 1.74Mg/m3 within a moisture content range of 2-3% being achieved for the hammer to be accepted.
A performance check has been conducted on a vibrating hammer proposed for use in the project. However, the required minimum dry density is not being achieved with an average dry density of 1.56Mg/m3 being measured in several performance checks. The hammer used is 1100W in excess of the required 600W with the load applied to the sample in the mould being 36kg, within the limits of 30-40kg. This check was repeated using different uncrushed sand samples from a site in Ireland that have been graded to the required specification (1kg of the soil retained on the 0.3mm sieve blended with 4kg of the soil retained on the 0.425mm sieve per sample) and the moisture content has been measured to be within the permitted range.
It is noted that in laboratory guidance by Head that the 1.74Mg/m3 value is only applicable for an unused sample of clean, dry silica sand from the Woburn Beds of the Lower Greensand in the Leighton Buzzard district and that other types of sand will give different results. Thus the thinking is that the specific gravity of the sand is affecting the result and not reaching compliance. It is noted that this is a Euronorm so I am curious to see has this resulted in queries by others.
Has anyone come across this previously or have insights on this topic? Any guidance would be much appreciated.
Post Your Answer
Answers

Dr. Costas Sachpazis
- 10 Nov 2025
Dear Daniel,
Please take a look at the embedded Links.
TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM
Please take a look and download my relevant report regarding your inquiry at:
https://geodomisi.com/Technical%20Analysis%20of%20Vibrating%20Hammer%20Performance%20Check.pdf
https://geodomisi.com/Technical%20Analysis%20of%20Vibrating%20Hammer%20Performance%20Check.docx
With Compliments,
Dr. Costas Sachpazis
Email: [email protected] & [email protected]
Specific Gravity of Stabilised Soils
Q&A
- 26 Jul 2025
Hi Everyone,
Im working as a Consultant Engineer and have observed Nuclear Density Test results along with Sand Replacement Results which are slightly above the Zero Air Voids Line on a soil stabilisation project. Testing has been done to confirm the specific gravity of the natural untreated soil alongside checks on site to verify same soil used and the equipment used is functioning correctly. I have hypothesised that the addition of a nominal quantity of cement as part of the soil stabilisation process has resulted in the specific gravity increasing and thus raising the zero air voids line. Calculating the quantity of cement with a specific gravity of 3.15 to obtain the specific gravity indicated by the results however does not tally with the binder used on site. Could the reasoning be that there is a chemical reaction undergoing that is affecting the specific gravity?
Has anyone come across this previously or have insights on this topic? Any guidance would be much appreciated.
Post Your Answer
Answers

Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company Course
29 Jul 2025

Get more out of PLAXIS by understanding and using advanced soil models as HSsmall and Soft Soil Creep and learn the advantages of 3D modelling for shallow, piled and piled raft foundation. Join the optional 4th day for an Introduction to dynamics and seismic engineering with PLAXIS.
Register
ISSMGE Symposium
07 Apr 2025
Read More

Bentley Systems Webinar
24 Jul 2025
Join this webinar to explore the foundations of onshore wind turbines, dive into offshore wind turbines supported by monopile and jacket foundations, and discover floating wind turbines anchored with suction buckets. Gain valuable insights into PLAXIS through an engaging and informative webinar.
Register Project Manager, Geotechnical Engineer
Project Manager, Geotechnical Engineer
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Civil - Project Management
Location: Washington, United States
 Construction QA / QC Supervisor
Construction QA / QC Supervisor
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Civil - Environmental, Construction - Project Manager, Construction - Estimator/Inspector
Location: Arizona, United States
 Geotechnical Engineer (Field Position)
Geotechnical Engineer (Field Position)
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Construction - Engineer
Location: Michigan, United States
 Project Civil Engineer - Private & Municipal
Project Civil Engineer - Private & Municipal
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Civil - Structural, Civil - Environmental, Civil - Hydraulic, Civil - Construction, Civil - Transportation , Civil-other
Location: Arizona, United States
 779055 - Early-Career Geotechnical Engineer
779055 - Early-Career Geotechnical Engineer
Field: Civil - Geotechnical
Location: Georgia, United States
 Sr. Marine Structural Engineer
Sr. Marine Structural Engineer
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Civil - Structural, Civil - Coastal
Location: Florida, United States
 Ports Engineer Practice Lead
Ports Engineer Practice Lead
Fields: Civil - Geotechnical , Civil - Environmental, Civil - Coastal
Location: Florida, United States



